SIP provides interoperability between different brands of codecs due to its standardized protocols for connecting different devices. The codec is fully EBU N/ACIP Tech 3326 compliant when connecting using SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) to other brands of IP codecs.
SIP is also a useful way of dialing another device and locating it easily. This task is usually performed by SIP servers, which communicate between SIP-compliant devices to set up a call. SIP connections can be made in two ways; registered or unregistered.
Unregistered Peer-to-Peer SIP Connections
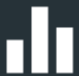
Codecs don’t need to be registered to a SIP server to dial peer-to-peer SIP connections. An unregistered SIP peer-to-peer connection involves two codecs connecting to each other directly using an IP address, as you would for a standard Tieline IP call. The difference is that a Tieline IP call uses proprietary Tieline session data to negotiate call parameters (e.g. algorithm and bit rate) when a call is established, whereas a peer-to-peer SIP connection uses Session Description Protocol (SDP) for this purpose. SIP provides interoperability between different brands of codecs due to its standardized protocols for connecting dissimilar devices and is used when connecting Tieline codecs to non-Tieline devices.
There are two very distinct parts to a call when dialing over IP. The initial stage is the call setup stage and this is what SIP and SDP is used for. The second stage is when data transfer occurs and this is left to the other protocols such as RTP/UDP to stream audio data. SDP works with a number of other protocols, to deliver the following functions when connecting devices over SIP:
• Establish a codec’s location.
• Determine the availability of a codec.
• Negotiate the features to be used during a call, e.g. the algorithm and bit rate.
• Provide call management of participants.
• Adjust session management features while a call is in progress (e.g. termination and transfer of calls).
All the mandatory EBU N/ACIP 3326 algorithms are supported in your Tieline codec, including G.711, G.722, MPEG-1 Layer 2 and 16 bit PCM, as well as optional algorithms including Opus, LC-AAC, AAC-LD, HE-AACv2 and aptX Enhanced. The default algorithm selected when connecting using SIP is G.711.
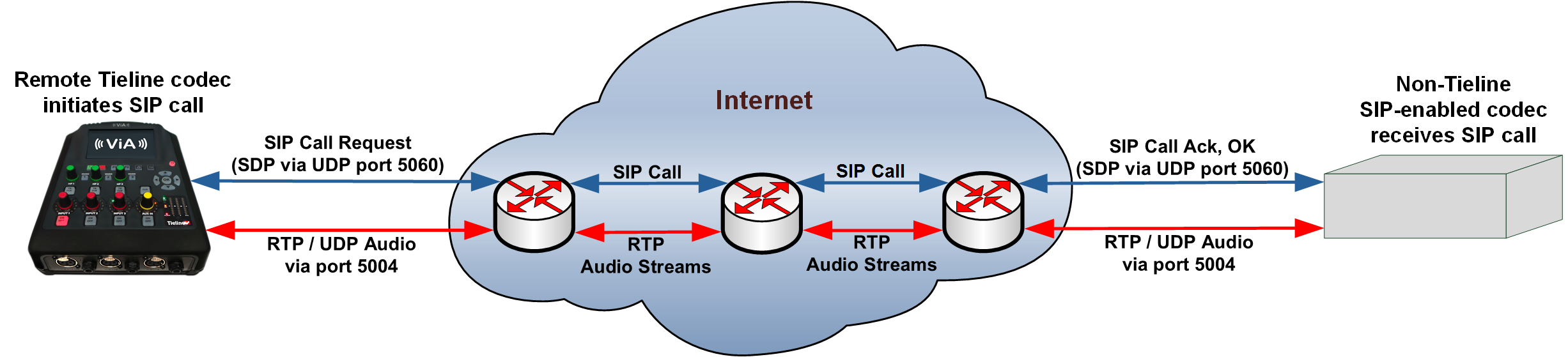
SIP Server Connections
The benefit of using a SIP server to connect is that any device can be ‘discovered’ via its SIP server registration. This is particularly useful if a codec is being used in multiple locations with IP addresses that are DHCP assigned. These DHCP addresses are unreliable and are not recommended for live broadcast connections. As long as your codec and the device you are dialing are both registered to a SIP server you can connect by simply dialing the destination SIP address.
Some SIP servers route RTP audio through the SIP server as well and Tieline recommends avoiding this type of server whenever possible. Otherwise you will be reliant on the SIP server for streaming broadcast audio packets and most servers are not designed for mission critical packet streaming.
To dial a codec via a SIP server requires:
1.Both devices to be registered with separate SIP accounts.
2.Both codecs configured to operate in SIP mode.
3.The IP address of the SIP server.
4.An IT administrator to open UDP port 5060 to enable SIP traffic, as well as UDP audio port 5004.
A SIP server administrator should be able to provide the following details to enable SIP registration of a device:
•Authenticating username
•SIP address
•Domain
•Realm
•Registrar
•Registar port
•Outbound Proxy
•Proxy port
Getting Started with SIP
To dial over SIP peer-to-peer without using a SIP server see Dialing SIP Peer-to-Peer. To dial over SIP using a SIP Server you will need to:
1.Register the codec to a SIP server using SIP account credentials.
2.Configure a SIP interface in the codec. Note: This SIP1 or SIP2 interface will include the proxy and port settings, as well as the selected IP interface used to make the connection, e.g. LAN1 or LAN2.
|
Important Notes: •The codec supports dialing over SIP using a registered SIP server account, or peer-to-peer using one of the two SIP interfaces SIP1 and SIP 2. •SIP dialing is only supported over point-to-point connections, not multi-unicast connections. •The codec supports a SIP call being placed on-hold. Note: there are several different implementations of "on-hold" by different SIP providers. Some will stop streaming when a call is placed on-hold and others will replace live streaming with on-hold messages or music. •Some ISPs and/or cellular networks may block SIP traffic over UDP port 5060. •Tieline G3 codecs do not support connections using algorithms like AAC, aptX Enhanced and Opus and will default to MPEG Layer 2 if an incoming call is configured to use these algorithms. •Failover and SmartStream PLUS redundant streaming are not available with SIP connections. •When connecting to a Tieline G3 codec using SIP you need to manually select the G3 audio reference level in the codec. To do this select Audio ▪Select either a mono or stereo profile ▪Select [Menu] > [Configuration] > [IP1 Setup] > [Session Type] > [SIP] ▪Select [Menu] > [Configuration] > [IP1 Setup] > [Algorithm] > [G711/G722 or MP2] |