
ISDN Module settings in the Transport Interfaces menu determine how an ISDN module operates at a particular site. Other answering-related settings are available in the Transport menu via Answering > [Select ISDN Config]. The codec displays ISDN line sync status in the Status Bar at the top of the TOUCH SCREEN.
|
Symbol |
Description of Status |
1 |
No ISDN Symbol |
No ISDN module is installed in the codec. |
2 |
|
An ISDN module is installed in the codec and either: •No ISDN line is attached to the codec, or •ISDN line is attached but line sync hasn't been detected by the module |
3 |
|
An ISDN module is installed in the codec and line sync has been detected. |
Configuring ViA ISDN Modules
To adjust ISDN module settings:
1.Press the HOME ![]() button to return to the Home screen and tap Settings
button to return to the Home screen and tap Settings  .
.
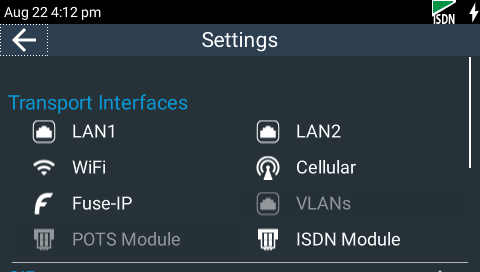
2.Tap Transport Interfaces to expand the menu if it is not displayed, then tap ISDN Module  to configure module settings.
to configure module settings.
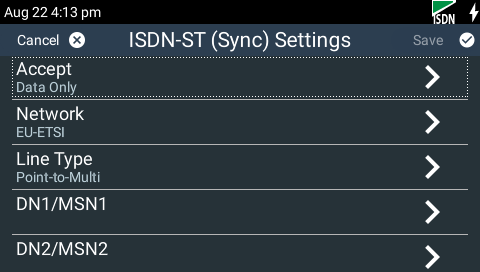
3.Tap Accept to adjust the type of calls the codec will accept.
|
Important Note: ISDN Sync should be displayed when an ISDN line is connected to the codec. This appears regardless of whether you have configured the ‘ISDN Line Type’ correctly. |
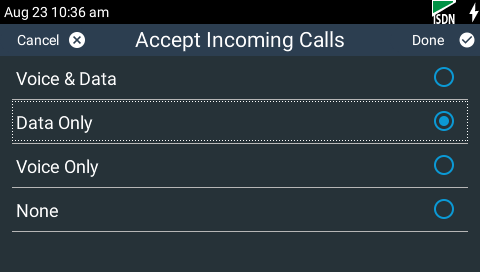
4.This menu is a call filter to allow or deny voice or data calls according to your preferences. By default Data Only is selected. Tap to accept or disallow voice or data calls according to your preferences.
|
Important Note: G.711 is the default algorithm for incoming connections when Voice Only is selected. There are two G.711 algorithms and the one used by the codec depends on the country setting in the codec. The µ-law algorithm is used in the USA, Japan and Canada, whereas the A-law algorithm is used in other countries. |
5.Tap Network to view Network Type options.
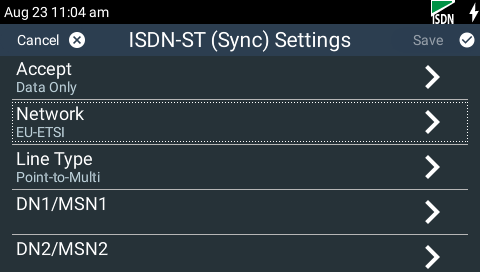
6.Tap to select the correct Network Type for the region in which you are using the codec.
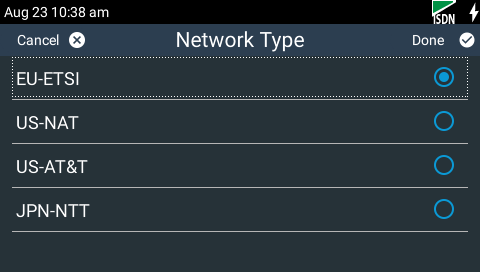
Networks |
Region |
EU-ETSI |
If Switch Type is ETSI (UK, Europe, Australia and most other countries) |
US-Nat |
If switch type is National ISDN-1 and 2 |
US-AT&T |
If switch Type is AT&T 5ESS |
JPN-NTT |
If you are in the Japan and your network is NTT |
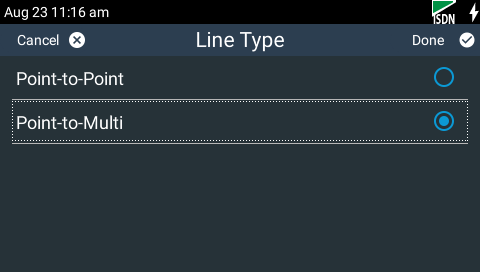
7.Tap Line Type to select whether your ISDN line is Point-to-Point or Point-to-Multipoint. This can be verified by asking your Telco.
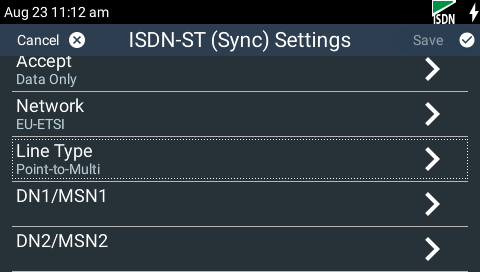
8.By default select Point-to-Multipoint, unless your switch type is point-to-point, your Telco says the line is point-to-point, or you are connected to a PABX system. Most PABX systems are point-to-point.
9.Tap to select each SPID, DN or MSN. If you are in the US enter DN and SPID numbers as required, or in other regions enter DN or MSN numbers as required. Note: SPID1 and SPID2 are only visible when a ViA (U) USA ISDN module is installed in the codec.
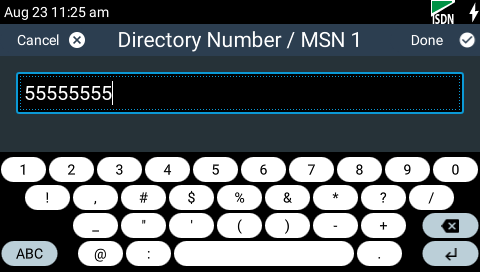
10.Use the on-screen keyboard to enter each number, then tap Done in the top right-hand corner of the TOUCH SCREEN to add each number.
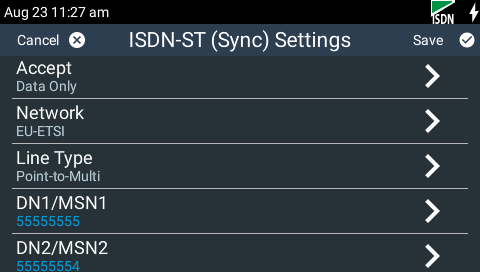
11.Tap Save in the top right-hand corner of the TOUCH SCREEN to confirm and store all entered numbers.
|
Important Notes:
Directory Numbers and Multiple Subscriber Numbers Directory Numbers (DN) in North America and Multiple Subscriber Numbers (MSN) in the rest of the world are simply phone numbers associated with an ISDN B channel, like lines listed in a typical phone directory. Your Telco will normally supply 2 DN/MSN numbers for each pair of B channels. However, these numbers may or may not be associated with a specific B channel.
Often broadcasters prefer to predict which B channel will answer an incoming call to ensure audio routing is consistent. However, if a DN or MSN number is not entered in the codec and multiple B channels are available, the codec may use any channel to answer an incoming call. To ensure calls are routed consistently, enter a DN/MSN number (without the country or area code) as the DN/MSN for a B channel, then only that corresponding B channel will answer an incoming call to that number. Programming DN/MSN numbers for each B channel allows the codec to ignore calls without matching DN/MSN numbers. This is the best way to answer calls from codecs in a predictable manner.
SPID Numbers in North America ISDN relies on an initialization procedure for associating Service Profiles with specific terminating equipment (e.g. your audio codec) rather than lines. In the US Telcos assign a Service Profile ID (SPID) number which assists in identifying different ISDN services across the network. Your Telco must provide a SPID for each B channel you order when connecting over US-Nat or US-AT&T networks in the US. A SPID is not required when using the AT&T PTP protocol.
Typically, each ISDN BRI service in the US will have two SPIDs and these must be entered correctly. When you enter a SPID into your codec and connect it to an ISDN line, an initialization and identification process takes place, whereby the terminating equipment (your codec) sends the SPID to the switch. The switch then associates the SPID with a specific Service Profile and directory number.
Note: SPID numbers normally include the phone number and additional prefix or suffix digits up to 20 digits long. |



