
To view and monitor any active connections:
1.Press the HOME ![]() button to return to the Home screen, then tap Connections.
button to return to the Home screen, then tap Connections.
2.To view Connection Details:
a.Tap the On Air  indication on the Connections screen, or
indication on the Connections screen, or
b.Swipe left on the Connections screen to reveal the Connection Details screen.
Tap the Statistics  button or swipe left again to view IP packet arrival statistics. Analysis is historic and assessed over 1minute and 10 minutes of connection time.
button or swipe left again to view IP packet arrival statistics. Analysis is historic and assessed over 1minute and 10 minutes of connection time.
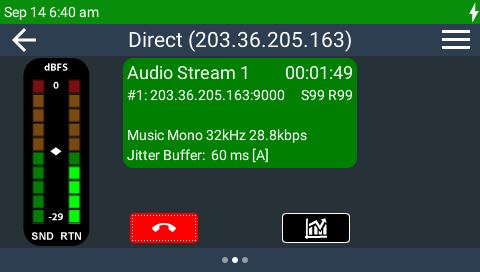
Connection Details screen

Statistics screen
Send/Return Link Quality
Send and Return link quality numbers in the Connection Details screen assist in determining if there is a problem at either end of a connection. For example, on an IP connection the Return reading represents the audio being received from the network locally (i.e. audio data is being sent by the remote codec). Conversely, the Send reading represents the audio data being sent by the local codec (i.e. being downloaded by the remote codec). To ensure a stable connection, try to maintain a reliable reading of 80 or higher for both the Send and Return reading.
|
Important Note: •The Return link quality reading is the same as the Local (L) setting displayed on a G3 codec. •The Send link quality reading is the same as the Remote (R) setting displayed on a G3 codec. |
|
Feature |
Description |
1 |
Lost Packets |
Packets sent that failed to arrive |
2 |
Empty (Jitter Buffer) |
Indicates how often the jitter buffer ‘reservoir’ empties causing loss of audio |
3 |
Late Packets |
The number of packets that arrive late, i.e. after audio play out |
4 |
FEC Packets |
Indicates the number of forward error correction (FEC) packets that have been replaced if it is enabled in the codec |
5 |
1 minute |
Statistics listed for the last minute of network activity |
6 |
10 minutes |
Statistics for the last 10 minutes of network activity |
|
Important Note: If the jitter buffer, FEC or the connection bit rate is changed, we recommend assessing a minute of recent connection performance in preference to 10 minutes of historical connection performance. 10 minutes of data will include connection settings which may no longer be relevant. ‘Packet arrival history’ is cleared when you hang up a connection. |
Following is a packet arrival analysis table with solutions for any noticeable packet loss statistics displayed on the screen.
Packet Analysis |
Displays |
Possible Causes |
Possible Solutions |
Loss |
Packets failed to arrive. |
•LAN/WAN congestion •Unreliable ISPs •Unreliable networks •Unreliable IP hardware |
•Renegotiate connection bit rate downwards •If link quality good, add or increase FEC as required •Assess ISPs QoS if very bad performance |
Empty |
Indicates how often the jitter buffer ‘reservoir’ empties causing loss of audio. |
•High number of packets being lost or arriving late •Signal dropouts using cell-phone networks •Renegotiation causes the jitter buffer reservoir to empty |
•Once could be an anomaly – assess lost & late packets •If many lost packets and network is unreliable – renegotiate bit rate and /or FEC down •If many late packets, increase jitter buffer |
Late |
The number of packets that arrive late and after audio play out. |
•Network congestion •Jitter Buffer depth is too low |
•Auto-jitter buffer will adjust automatically •For manual jitter buffer settings, increase jitter buffer depth 50-100 ms & reassess (if only a few packets arrive late over time; audio repairs will be automatic and may not require buffer changes). |
FECd |
Indicates the number of FEC repaired packets if FEC active. |
•Packets have been lost or corrupted over the network |
•Assess audio quality & the number of FEC repairs – if many packets are being ‘lost’, perhaps reduce FEC &/or renegotiate bit rate down. |

