
Open the HTML5 Toolbox Web-GUI and click Transport and then click Network to view and configure Ethernet and VLAN interface settings in the Web-GUI.
|
Important Note: For assistance with configuration of IPv4 or IPv6 network connections contact your IT Administrator. |
IPv4 versus IPv6
An IP address is a unique address to identify a device on a TCP/IP network. Your codec uses dual IP protocol stacks to allow your codec to work on both IPv4 and IPv6 networks. Tieline codecs support both DHCP (default) IP addressing and static IP addresses for dialing IPv4 connection endpoints.
If you want to dial a codec with a public IP address you simply dial the IP address to connect. If you want to dial a codec with a private IP address you need to perform network address translation (NAT). NAT allows a single device, such as a broadband router, to act as an agent between the public internet and a local private LAN. Usually this will be set up at the studio end so you can dial into the studio from the remote codec.
Support for IPv6 connections allows you to use IPv6 infrastructure to connect to other codecs globally.
Configuring Ethernet Ports and VLANs
The codec features two physical Ethernet LAN ports, two USB ports and up to four additional VLAN interfaces.
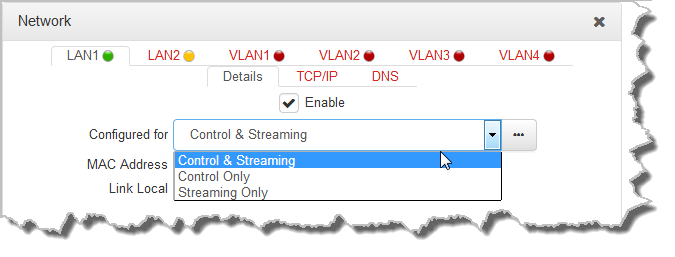
VLAN interfaces have features similar to physical Ethernet interfaces. However, your network administrator will need to configure VLAN support throughout your network for them to be supported in your codec. These interfaces can be configured to stream or control the codec, or do both.
As an example, if only one physical Ethernet interface is available, VLANs or USB interfaces can be used to stream SmartStream PLUS audio or separate codec control and streaming functions as required. IP interfaces can be configured for:
•Controlling audio: codec control and command only from a selected IP interface.
•Controlling and Streaming: stream audio and control and command the codec from a selected IP interface.
•Streaming audio: stream audio only from a selected IP interface.
•Nothing: Disable the Ethernet port from streaming audio and codec command and control (VLANs only).
Select the Details tab in the Network panel to edit control and streaming settings. Select the Enable check-box to activate each interface. LAN1 and LAN2 are enabled by default. Note: An interface with a green status indication is enabled and has an active LAN cable attached. A LAN interface with red text and a yellow status indication is enabled, however a network cable is not attached, e.g. LAN2 in the following image. An interface in red text with a red status indication is disabled, e.g. VLANs in the following image.
IPv4 Address Configuration
Click to select the TCP/IP tab in the Network panel to configure settings. The codec is capable of automatic DHCP address assignment, or manually configured static IPv4 address configuration via the drop-down Configure IPv4 drop-down menu. If you want to ignore IPv4 settings select Off.
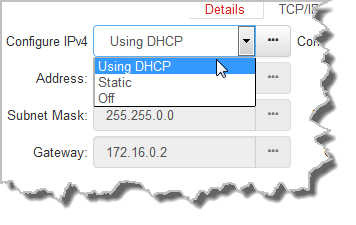
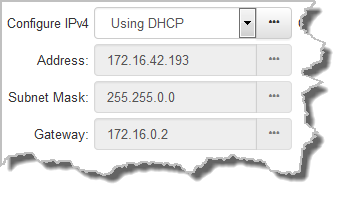
DHCP IP addresses are automatically assigned and can change each time you connect to your Internet Service Provider, or to your own local area network (LAN). By default the codec is configured for DHCP-assigned IP addresses.
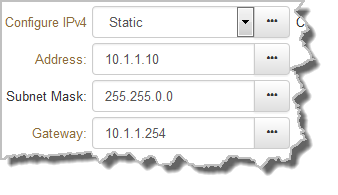
Static IP addresses are fixed addresses that are recommended for studio installations, so that IP address dialing remains the same over time for incoming codec connections.
Click Save to store all configuration settings.
|
Note: The Subnet Mask is used by the TCP/IP protocol to determine whether a host is on the local subnet or on a remote network. The default Gateway is the router linking the codec's subnet to other networks. See your IT administrator for more details. |
IPv6 Address Configuration
An IPv6 address is represented by 8 groups of 16-bit hexadecimal values separated by colons (:). The drop-down Configure IPv6 menu provides three address configuration options:
1.Automatically: An address is automatically assigned to the codec when you connect the codec to an IPv6 router. This process is similar to how an IPv4 DHCP address is assigned.
2.Manually: Select to enter static IPv6 address details.
3.Off: Select to ignore IPv6 address details.
|
Important Note: Select Off in the Configure IPv6 drop-down menu if you are not using IPv6 to connect to another device. This ensures your codec will attempt to connect using IPv4 at all times. |
Types of IPv6 Addresses
There are two types of addresses displayed in the IPv6 section:
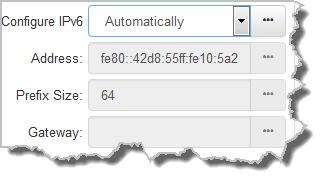
1.IPv6 address (normally global): A router-allocated IP address with 'global' visibility, details of which are displayed in the Address, Prefix size and Gateway text boxes.
2.Link Local: A local address which can only be used to connect to another device directly over a LAN. This address is allocated by the codec internally based on MAC address details.
Auto Address Assignment
By default the codec is configured for connecting to an IPv6 router which automatically allocates IPv6 address details, as displayed in the following example.
Manual IPv6 Address Assignment
1.To configure IPv6 address details into the codec manually, select Manually and enter details into the Address, Prefix and Gateway text boxes.
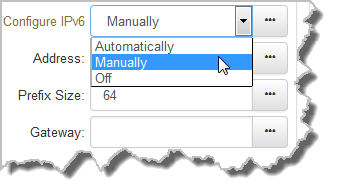
2.Click Save to store all configuration settings.
Specifying DNS Settings
It is possible to specify Domain Name Server (DNS) settings to allow easy look up of codecs within the specified DNS Addresses or Domains.
1.Select the DNS tab in the Network panel to configure settings.
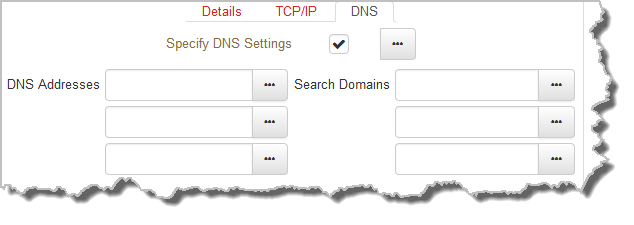
2.Click Save to store all configuration settings.
IP Via Mapping
When dialing over IP you can select the preferred interface to use when establishing a connection. By default Any is selected, which means the first available interface will be used to dial a connection. The default Via interfaces in order of use when available are:
1.LAN1 Ethernet port (default Primary Via interface)
2.LAN2 Ethernet port (default Secondary Via interface)
3.Internal built-in Wi-Fi (default Tertiary Via interface)
|
Important Note: VLAN interfaces have features similar to physical Ethernet interfaces. However, your network administrator will need to configure VLAN support throughout your network for them to be supported in your codec. |
Reconfigure Default Primary, Secondary and Tertiary Interfaces
It is possible to reconfigure the default Primary (LAN1), Secondary (LAN2) and Tertiary (Wi-Fi) interfaces in the codec. As an example, you may want to select Primary as the dialing interface in a program and then copy this program onto multiple codecs. However, the actual primary interface used at each location can vary for each codec. For one codec it may be a LAN interface and for another it may be a USB cellular interface. This allows you to configure site-specific settings to suit the available network interfaces at different remote locations.
1.Open the HTML5 Toolbox Web-GUI and click Settings and then click IP Via Mapping to open this panel.
2.Click the drop-down arrow for each interface to select the preferred default setting.
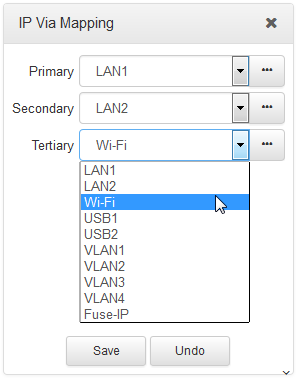
3.Click Save to store the configuration.
|
Important Note: Fuse-IP cannot be configured as a default Primary, Secondary or Tertiary Via. |
Configuring QoS
The codec can be configured to tag IP data packets sent across a network by entering a value into the Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) field within the header of data packets transmitted over the network.
1.Open the HTML5 Toolbox Web-GUI and click Settings and then click Options to open the Options panel.
2.Click in the DSCP field and enter the priority setting recommended by your IT administrator.
3.Click Save to store configuration settings.
|
Important Note: Check with your IT administrator before changing this setting. By default the codec is configured for Assured Forwarding and more details about DSCP are available on Wikipedia at http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dscp. |

