Product |
Feature |
Notification |
Gateway 4 |
Multicasting |
Supports 1 or 2 multicast server and/or client streams being sent to unlimited endpoints |
Gateway 8/16 |
Multicasting |
Supports up to 8 different multicast server and/or client streams in Gateway 8, and up to 16 different multicast server and/or client streams in Gateway 16 |
In multicast server mode a 16 channel Gateway codec supports sending 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8 or 16 multicast audio streams to unlimited endpoints over compatible IP networks. It is also possible to use multicast client mode to simultaneously receive up to 16 separate multicast streams.
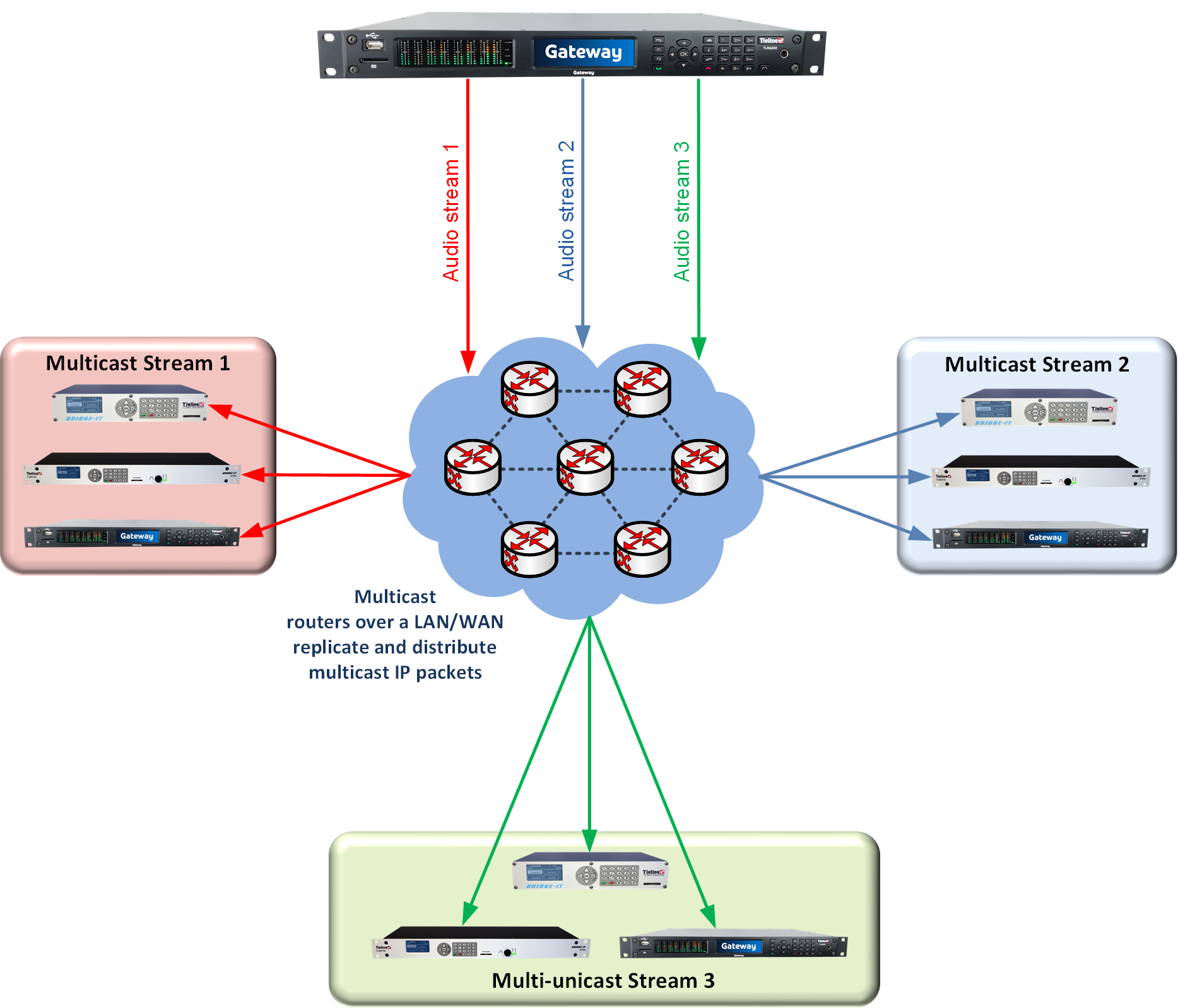
Gateway codec in 3 x multicast server mode distributing 3 multicast IP streams
How Multicasting Works
Multicast transmissions are sent using a dedicated IP multicast address that looks similar to a regular IP address and multicast subscribers request transmissions from this address. This unique address allows multicast routers to identify multicast requests from a group of codecs interested in a particular transmission and packets are replicated depending on demand. This can create large demands on network bandwidth if the multicast group is significant in size.
As a result, only small sections of the internet are multicast enabled and many internet service providers (ISPs) block multicast traffic over wide area networks. This restricts most multicast broadcasts to private local area networks. Some ISPs provide quality of service (QoS) priority to multicast streams for an increased service charge. You need to check with your ISP to find out what multicast services, if any, are available over WANs.
|
Important Notes: •When a connection is dialed Tieline codecs normally use session data to configure settings like the algorithm, connection bit rate and sample rate etc. Multicast connections do not use session data and it is imperative that all codecs are configured with the same connection settings prior to connecting, or they will not be able to join multicast streaming sessions. •Automatic or fixed jitter buffer settings can be adjusted on individual client codecs as required. There is no jitter buffer setting on the server codec because it never receives audio packets. |
Multicast Server versus Multicast Client Programs
Two different types of multicast programs need to be created when multicasting:
•A multicast server program is used by the broadcasting codec to send multicast IP packets to multicast routers on a network.
•A multicast client program is used by codecs to receive multicast IP audio packets.
A multicast server codec sends audio packets only and a multicast client codec receives audio packets only. Codecs using the client program request multicast packets (sent from the server codec), which are distributed by multicast routers.
Creating Multicast Server Programs
|
Important Notes: Before you start program configuration please note: •Ensure all connection related settings like the port, algorithm, bit rate (etc) match on both multicast server and client programs or they will not connect successfully. •You cannot edit a program when it is currently loaded in the codec. •Lock a loaded custom program or multistream program in a codec to ensure it cannot be unloaded by a codec dialing in with a different type of program. For example, if a multistream program is not locked it will be unloaded by a mono or stereo call. •Some drop-down menus and settings may be greyed out intentionally depending on features available. •It is possible to save a program at several points throughout the program wizard and use default settings to save configuration time. •Always dial the multicast server codec connection first before connecting multicast client codecs. •Multicast client codecs will display return link quality (LQ) only. The Return reading represents the audio being downloaded from the network locally. Multicast server codecs do not display LQ readings. •The default UDP audio port setting is 9000 for the first multicast, 9010 for the second multicast and 9020 for the third multicast, and so on. E.g. if a client codec wishes to receive multicast audio stream 2 then it must use audio port 9010. Default Tieline Audio Stream ports are outlined in Default Program Ports. •Use firmware higher than 2.8.xx in the Bridge-IT, Genie and Merlin families of codecs to transmit auxiliary data. •Relay functionality is available for multicast connections between Tieline codecs. •It is not possible to connect to a G3 codec and receive multicast IP audio streams. |
1.Open the HTML5 Toolbox Web-GUI and click Connect in the Menu Bar, then select Program Manager to launch the Program Manager panel.
2.Click the New Program button to open the wizard and:
•Click in the text box to name the new program.
•Click the Mix drop-down arrow to associate a custom matrix mix with the program if required.
•Select a preferred Multicast Server program for the options available.

•If you want to use an existing program as a template, select this option. Then click Next.

|
Important Notes: When you decide to use an existing program as a template, the new program inherits all the settings of the template program and you can adjust these settings as required by continuing through the program wizard. |
3.To configure new program level rules click the drop-down arrow and select the preferred option from those available. Click the blue Plus symbol  to add a new rule and click the Minus symbol
to add a new rule and click the Minus symbol  to remove a rule.
to remove a rule.

|
Important Notes for Rules: •The Gateway 4 codec has 8 hardware GPIOs and 56 logical outputs, and the Gateway 8/16 has 16 hardware GPIOs and 48 logical outputs; both codecs also have 3 virtual inputs, and 64 Livewire GPIOs, or 64 WheatNet Logic Inputs/Outputs. (WheatNet logic I/Os allow Tieline WheatNet-IP enabled codecs to activate functions across a WheatNet-IP network. WheatNet logical inputs are only available if a codec has a WheatNet-IP card installed). See Enabling Relays & RS232 Data for more info. •A non-WheatNet-IP Tieline codec can be configured to trigger a WheatNet LIO in a Tieline WheatNet-IP codec. •Tieline WheatNet-IP codecs require Wheatstone Razor firmware version 1.4.22 or later to support WheatNet LIOs. In addition, the WheatNet-IP codec must have the WNet Enable LIO checkbox selected in the Options panel of the HTML5 Toolbox Web-GUI. •The Enable Livewire GPIO checkbox must be selected in the Options panel of the HTML5 Toolbox Web-GUI to use Livewire GPIOs. •Relay reflection is not available for SIP and Multicast Client programs. •Connection-related rules are not displayed in Answer only audio streams. •Rules intended to activate dialing will not be valid in Answer only programs or audio streams. •For more details about rules see Creating Rules. |
4.Enter the Stream Name, then click Next.

5.This audio stream connection in the wizard will allow the codec to dial. Enter the name of the connection in the text box, then click Next.

6.Configure the transport settings for the connection, then click Next. Note: select UDP/IP +RTP for RFC compliant streaming.

|
Important Note: •The encode and decode direction is configured automatically for Encode Only (server program) or Decode Only (client program). This setting is configured when either Multicast Server or Multicast Client is first created in the wizard. •The Time to Live (TTL) value you need to use is dependent upon your network infrastructure. Please consult your network administrator if you are unsure about how to configure this setting. •Use firmware higher than 2.8.xx in the Bridge-IT, Genie and Merlin families of codecs to enable auxiliary data. |
7.Configure the multicast IP address and Remote Audio Port (the same multicast address and port must be used for both the server and client programs), then specify which IP streaming interface is used to dial this connection, e.g. Primary (port LAN1) or Secondary (port LAN2), then click Next. Note: By default Any will select LAN1 if it is available and LAN2 if it is unavailable.

8.Click the drop-down arrows on the right-hand side of each text box to select the Encoding, Sample rate, Bit rate or Sample size options. Click Next to continue.

9.Click the drop-down arrow for Send FEC Type to enable RFC-compliant FEC. Configuration instructions are displayed in the right-hand Program Manager panel pane. FEC Delay is only available when the FEC percentage is 100%. This is designed to delay the sending of FEC packets for a predetermined period after the primary audio stream's packets are sent. This will increase the likelihood that the FEC packets will take an alternate route to the primary stream's packets. This means that if primary audio stream packets are not received at the remote codec, there is a good chance that FEC packets taking an alternate route will be received and replace them. When a FEC percentage lower than 100% is configured, FEC packets are automatically delayed based on the ratio of primary packets to FEC packets sent.

10.Click Next to select configure Enable Auto Reconnect if required.

11.Next you can either:
i.Click Next to configure rules options.
ii.Click Next Stream if configuring multiple audio stream programs.
12.To configure new stream level rules click the drop-down arrow and select the preferred option from those available. Click the blue Plus symbol  to add a new rule and click the Minus symbol
to add a new rule and click the Minus symbol  to remove a rule.
to remove a rule.

13. After configuring all streams in the multicast server program click Save to store the program settings, then click Finish.
|
Important Notes: There is no jitter buffer setting on the server codec because it never receives audio packets. |
14.Configure multicast server and multicast client programs and load all codecs with the appropriate program. Dial the multicast server program connection first and then connect multicast client codec programs to begin receiving multicast audio packets. Select and connect audio streams in a program using the Connections panel, or dial the program manually using the codec front panel.
